This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Kubernetes v1.31: New Kubernetes CPUManager Static Policy: Distribute CPUs Across Cores
In Kubernetes v1.31, we are excited to introduce a significant enhancement to CPU management capabilities: the distribute-cpus-across-cores option for the CPUManager static policy. This feature is currently in alpha and hidden by default, marking a strategic shift aimed at optimizing CPU utilization and improving system performance across multi-core processors.
Understanding the feature
Traditionally, Kubernetes' CPUManager tends to allocate CPUs as compactly as possible, typically packing them onto the fewest number of physical cores. However, allocation strategy matters, CPUs on the same physical host still share some resources of the physical core, such as the cache and execution units, etc.
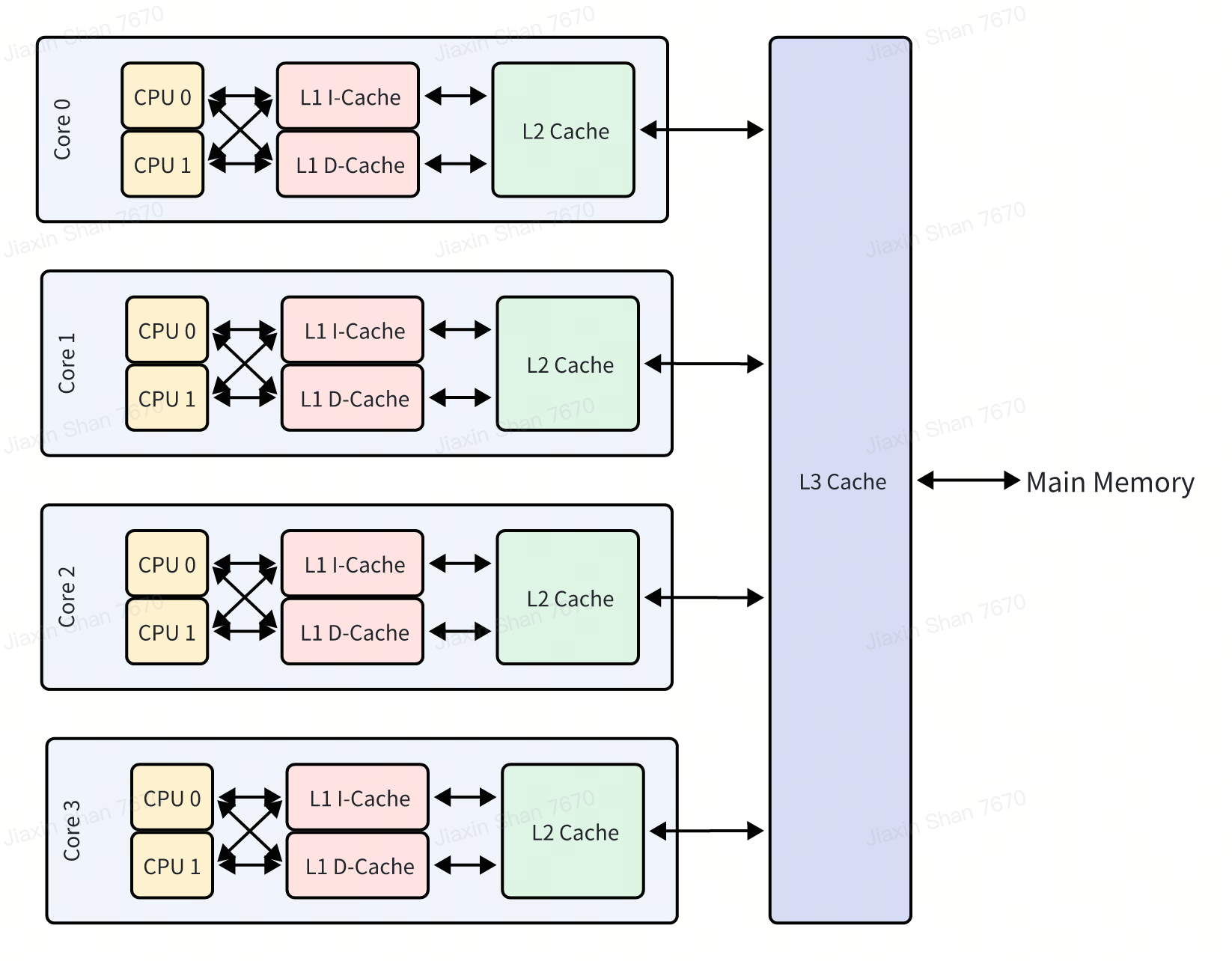
While default approach minimizes inter-core communication and can be beneficial under certain scenarios, it also poses a challenge. CPUs sharing a physical core can lead to resource contention, which in turn may cause performance bottlenecks, particularly noticeable in CPU-intensive applications.
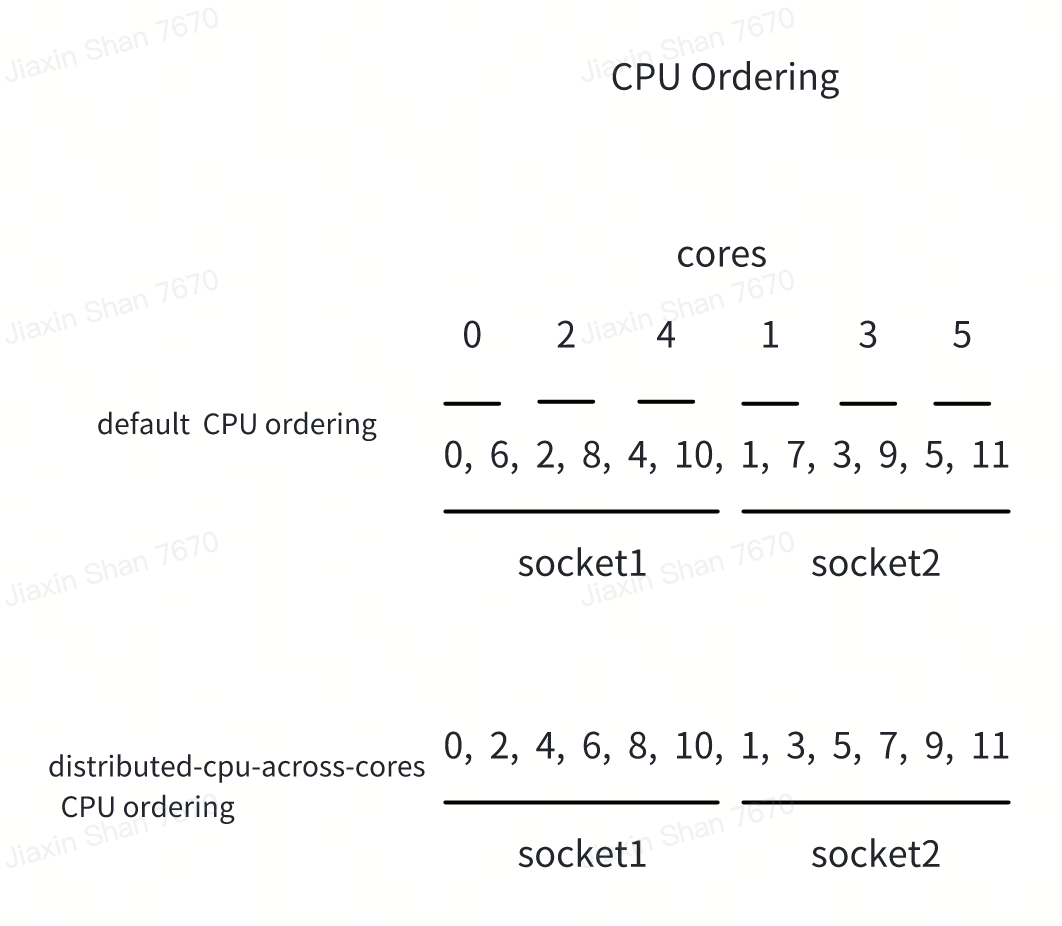
The new distribute-cpus-across-cores feature addresses this issue by modifying the allocation strategy. When enabled, this policy option instructs the CPUManager to spread out the CPUs (hardware threads) across as many physical cores as possible. This distribution is designed to minimize contention among CPUs sharing the same physical core, potentially enhancing the performance of applications by providing them dedicated core resources.
Technically, within this static policy, the free CPU list is reordered in the manner depicted in the diagram, aiming to allocate CPUs from separate physical cores.
Enabling the feature
To enable this feature, users firstly need to add --cpu-manager-policy=static kubelet flag or the cpuManagerPolicy: static field in KubeletConfiuration. Then user can add --cpu-manager-policy-options distribute-cpus-across-cores=true or distribute-cpus-across-cores=true to their CPUManager policy options in the Kubernetes configuration or. This setting directs the CPUManager to adopt the new distribution strategy. It is important to note that this policy option cannot currently be used in conjunction with full-pcpus-only or distribute-cpus-across-numa options.
Current limitations and future directions
As with any new feature, especially one in alpha, there are limitations and areas for future improvement. One significant current limitation is that distribute-cpus-across-cores cannot be combined with other policy options that might conflict in terms of CPU allocation strategies. This restriction can affect compatibility with certain workloads and deployment scenarios that rely on more specialized resource management.
Looking forward, we are committed to enhancing the compatibility and functionality of the distribute-cpus-across-cores option. Future updates will focus on resolving these compatibility issues, allowing this policy to be combined with other CPUManager policies seamlessly. Our goal is to provide a more flexible and robust CPU allocation framework that can adapt to a variety of workloads and performance demands.
Conclusion
The introduction of the distribute-cpus-across-cores policy in Kubernetes CPUManager is a step forward in our ongoing efforts to refine resource management and improve application performance. By reducing the contention on physical cores, this feature offers a more balanced approach to CPU resource allocation, particularly beneficial for environments running heterogeneous workloads. We encourage Kubernetes users to test this new feature and provide feedback, which will be invaluable in shaping its future development.
This draft aims to clearly explain the new feature while setting expectations for its current stage and future improvements.
Further reading
Please check out the Control CPU Management Policies on the Node task page to learn more about the CPU Manager, and how it fits in relation to the other node-level resource managers.
Getting involved
This feature is driven by the SIG Node. If you are interested in helping develop this feature, sharing feedback, or participating in any other ongoing SIG Node projects, please attend the SIG Node meeting for more details.